Develop, Deploy, and Test Apps with Expo Development Client

Erin Bailey
Flutter is Google’s mobile app SDK for crafting high-quality native interfaces on iOS and Android in record time. Flutter works with existing code, is used by developers and organizations around the world, and is free and open source.
For users, Flutter makes beautiful app UIs come to life. For developers, Flutter lowers the bar to entry for building mobile apps. It speeds up the development of mobile apps and reduces the cost and complexity of app production across iOS and Android. For designers, Flutter helps deliver the original design vision, without loss of fidelity or compromises. It also acts as a productive prototyping tool.
To install and run Flutter, your development environment must meet these minimum requirements:
[crayon-69a2c2893407d035505070 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><br />[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934082793854219 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><br />[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934086242643679 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><br />[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893408a924432043 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893408e828281520 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934092832999248 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
Clone alpha branch from Flutter repository using Git and add bin folder to your PATH.
[crayon-69a2c28934096972892756 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 |
<em>$ git clone https://github.com/flutter/flutter.git -b alpha $ export PATH=`pwd`/flutter/bin:$PATH</em> |
[crayon-69a2c2893409c407197902 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
The above command sets your PATH variable temporarily, for the current terminal window. You are now ready to run Flutter commands!
[crayon-69a2c289340a0999071993 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
Note: To permanently add Flutter to your path, see the reference https://flutter.io/setup-macos/#update-your-path.
[crayon-69a2c289340a3518741714 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340a7413640354 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
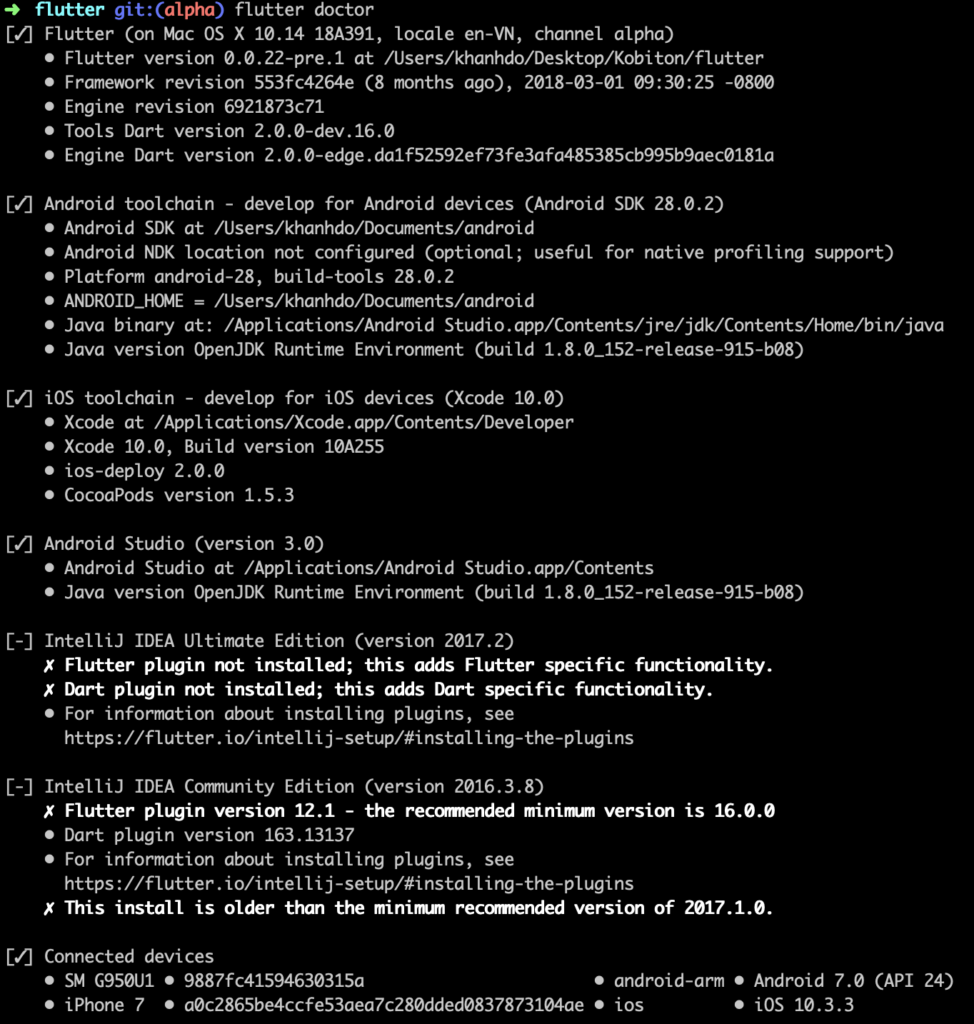
Run the following command to see if there are any dependencies you need to install to complete the setup:
[crayon-69a2c289340ab690267913 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 |
<em>$ flutter doctor</em> |
[crayon-69a2c289340b2813238023 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
This command checks your environment and displays a report to the terminal window. The Dart SDK is bundled with Flutter; it is not necessary to install Dart separately.
[crayon-69a2c289340b6239873818 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
For example:
[crayon-69a2c289340ba023348264 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340be674259558 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340c1279827343 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
macOS supports developing Flutter apps for both iOS and Android. Complete at least one of the two platform setup steps now, to be able to build and run your first Flutter app.
[crayon-69a2c289340c5222715697 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340ca437893168 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340ce460929480 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To develop Flutter apps for iOS, you need a Mac with Xcode 9.0 or newer:
[crayon-69a2c289340d1696041495 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340df814802552 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<br />[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340e3265251029 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340e6758496099 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"][/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340ea529567798 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
With Xcode, you’ll be able to run Flutter apps on an iOS device or on the simulator.
[crayon-69a2c289340ee819037995 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340f2910217083 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To deploy your Flutter app to a physical iOS device, you’ll need some additional tools and an Apple account. You’ll also need to set up physical device deployment in Xcode.
[crayon-69a2c289340f5731889525 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289340f8430410914 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 3 4 |
<em>$ brew</em> update $<em> brew install --HEAD libimobiledevice $ brew install ideviceinstaller ios-deploy cocoapods $ pod setup</em> |
[crayon-69a2c289340fc221398903 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
If any of these commands fails with an error, run brew doctor and follow the instructions for resolving the issue.
[crayon-69a2c28934100707570416 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934103860078714 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893410f207551275 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"][/crayon]


[crayon-69a2c2893411f850893938 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><br />[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934121012000083 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934124606152339 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934127715837930 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893412a085008570 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893412c172438880 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893412f910691607 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934132813668955 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934135747350146 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To prepare to run and test the Flutter app on an Android device, you’ll need an Android device running Android 4.1 (API level 16) or higher.
[crayon-69a2c28934137551027669 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893413c764363907 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893413f635083492 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
By default, Flutter uses the version of the Android SDK where your adb tool is based. If you want Flutter to use a different installation of the Android SDK, you must set the environment[crayon-69a2c28934142090688466 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]ANDROID_HOME variable to that installation directory.[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934145966571229 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934147293569206 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"][/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893414a987951066 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c2893414d124739101 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
Here I created a sample flutter_app project using following terminal command:
[crayon-69a2c28934150162454530 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 |
<em>flutter create flutter_app cd flutter_app</em> |
[crayon-69a2c28934154495644300 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934157420167122 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To list out all connected devices, please use the commandflutter devices to show all:
[crayon-69a2c2893415b862949877 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 |
<em>SM G950U1 • 9887fc41594630315a • android-arm • Android 7.0 (API 24) iPhone 7 • a0c2865be4ccfe53aea7c280dded0837873104ae • ios • iOS 10.3.3</em> |
[crayon-69a2c28934162893310164 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
If you have only one device is connected, just use the command flutter run to install your app into the device.
[crayon-69a2c28934166650436317 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
Otherwise, if have more than one device connected; please specify a device with the ‘-d <deviceId>’ flag, or use ‘-d all’ to act on all devices.
[crayon-69a2c2893416a926318035 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 |
<em>flutter run -d 9887fc41594630315a flutter run -d a0c2865be4ccfe53aea7c280dded0837873104ae</em> |
[crayon-69a2c28934170729221884 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
Note: For iOS device, if you see the error as below, please double check the iOS Setup step to fix it.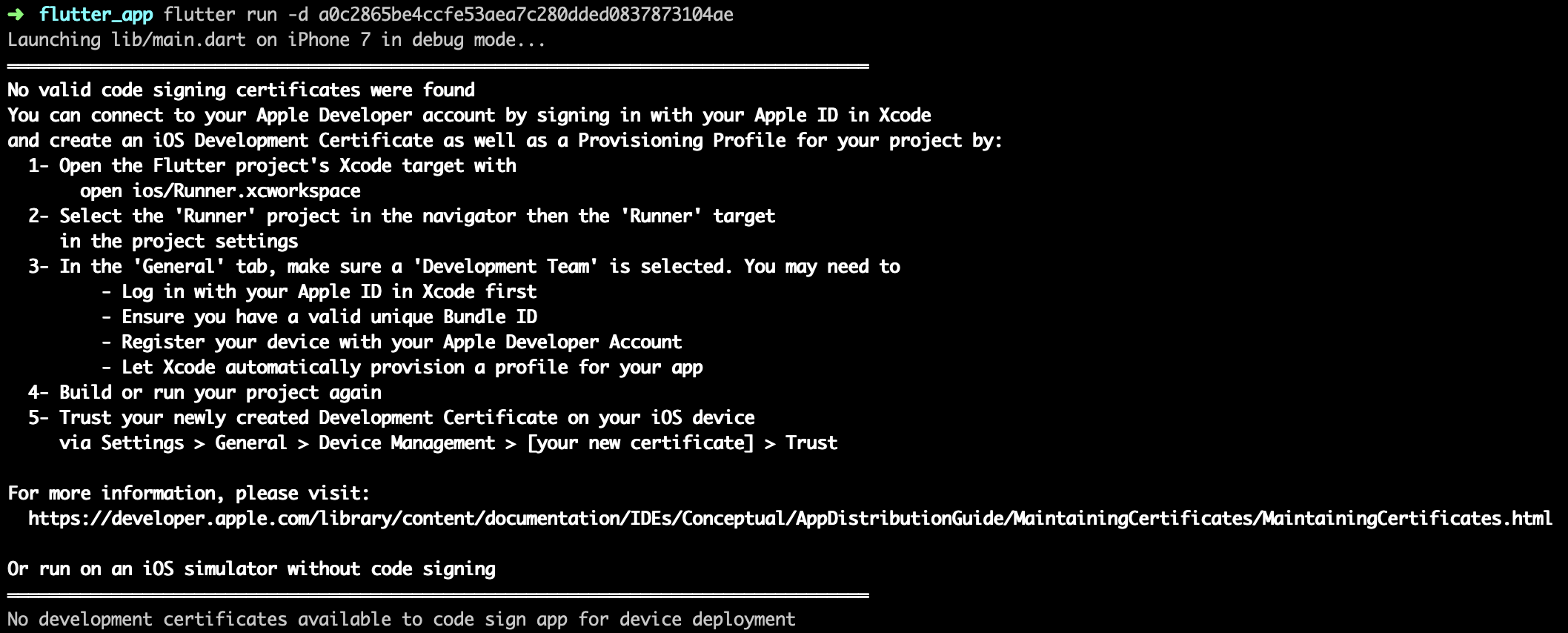
[crayon-69a2c28934174839668773 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c28934178633660464 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To generate an APK file, run:
[crayon-69a2c2893417c847683636 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 |
flutter build apk |
[crayon-69a2c28934182571149411 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
The output looks like:
[crayon-69a2c28934186653788175 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 3 4 5 |
Initializing gradle... 4.4s Resolving dependencies... 2.2s Running 'gradlew assembleRelease'... Skipping AOT snapshot build. Fingerprint match. Built build/app/outputs/apk/release/app-release.apk (7.6MB). |
[crayon-69a2c2893418c476321276 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
To generate an IPA file, run:
[crayon-69a2c28934191947755340 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 |
flutter build ios |
[crayon-69a2c28934197337357260 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
The output looks like:
[crayon-69a2c2893419b879762150 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
|
1 2 3 4 |
Building com.example.flutterApp for device (ios-release)... Automatically signing iOS for device deployment using specified development team in Xcode project: 4X2699XXXX Running Xcode build... 23.5s Built /build/ios/Release-iphoneos/Runner.app |
[crayon-69a2c289341a1286071255 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289341a6885827408 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
In this part, I will guide you how to use Kobiton Cloud to test your apps. A Kobiton account is required to access Kobiton system. If you do not have a Kobiton account yet, go ahead to create a free trial account and sign in. It takes just a few moments.
[crayon-69a2c289341cf823908994 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]

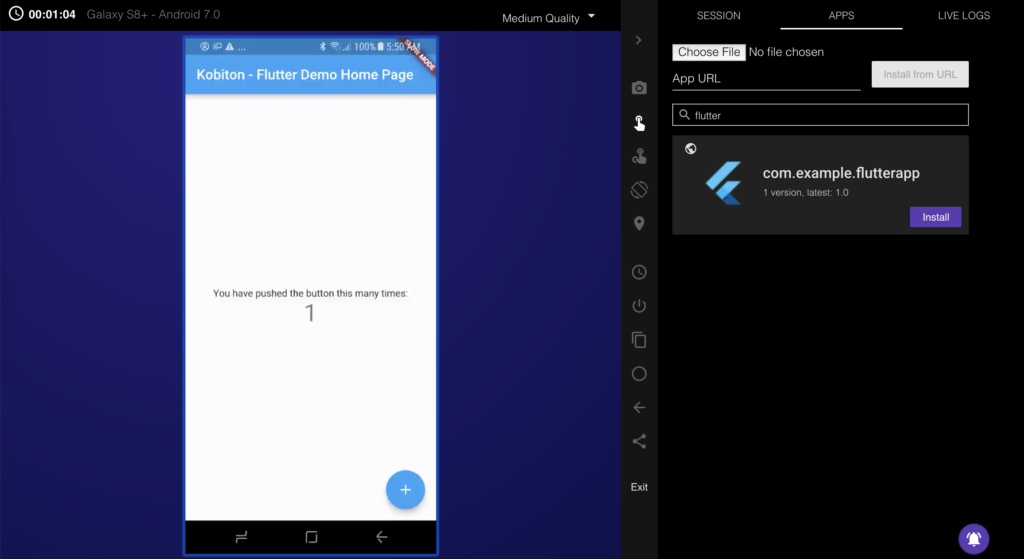
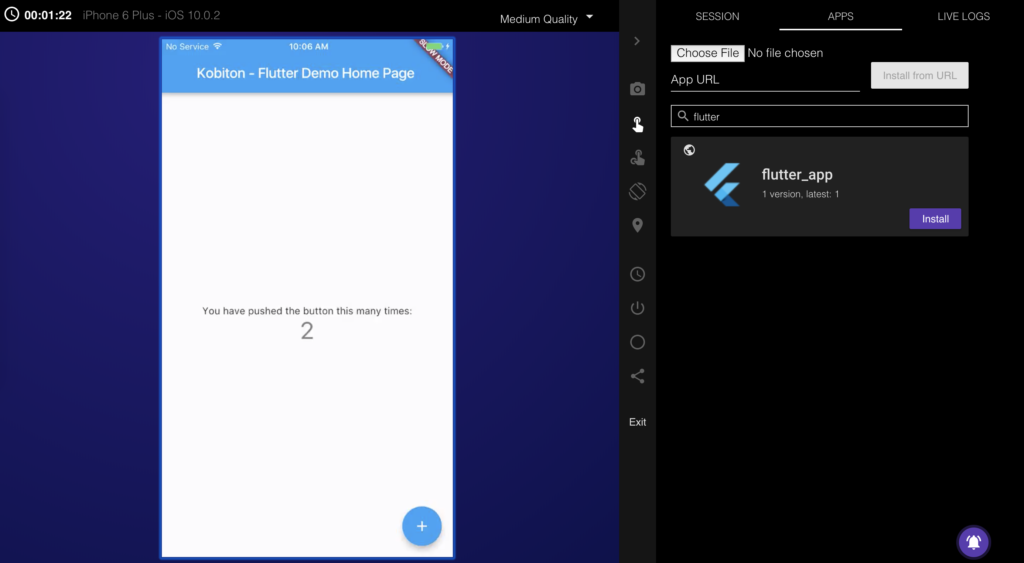
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<em>DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities(); capabilities.setCapability("app", "kobiton-store:1024"); capabilities.setCapability("deviceGroup", "KOBITON"); capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "Galaxy S8+"); capabilities.setCapability("platformVersion", "7.0"); capabilities.setCapability("platformName", "Android"); </em> |
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 |
<em>DesiredCapabilities capabilities = new DesiredCapabilities(); capabilities.setCapability("app", "kobiton-store:1024"); capabilities.setCapability("deviceGroup", "KOBITON"); capabilities.setCapability("deviceName", "iPhone 6 Plus"); capabilities.setCapability("platformVersion", "10.0.2"); capabilities.setCapability("platformName", "iOS");</em> |
[crayon-69a2c289341d8964435254 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289341dc072479273 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]
[crayon-69a2c289341e2512320115 inline="true" class="highlighter-rouge"]<code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge"><code class="highlighter-rouge">[/crayon]